By: ca.jackery.com
In recent years, solar power has gained significant popularity due to lower costs and technological advancements. With increased manufacturing and government incentives, solar systems are more affordable for homeowners and businesses. This eco-friendly energy source reduces air and water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. For many Canadians looking to reduce their carbon footprint, installing a solar system is a smart choice.
From a financial perspective, installing a solar battery charger and panels can result in significant savings on monthly utility bills, enabling individuals and businesses to produce their own electricity. Owning a home generator also allows for surplus electricity, which can be sold back to the grid through net metering programs, providing additional income. Installing solar panels from reliable manufacturers like Jackery may also increase a property’s value. Moreover, solar systems provide energy independence, self-reliance, and reliability.
However, choosing the right solar battery charger is crucial. Understanding battery compatibility, charge controllers, power requirements, durability, efficiency, and scalability will help you make the right investment.
Understanding Solar Battery Chargers
The right size solar generator should be chosen depending on specific needs. So, let’s explore what a solar battery charger is and how you can choose the right one for yourself.
A solar battery charger uses solar energy to charge batteries. It includes solar panels that capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy, which is stored in batteries for later use. These chargers are used for various batteries in household appliances, electronic devices, vehicles, and large-scale energy storage systems.
Here’s how a solar battery charger works:
- Solar Panels Capture Sunlight: Photovoltaic cells in the solar panels, usually made of silicon, convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Charge Controller Regulates Power: The charge controller regulates the electricity flow from the solar panels to the battery, preventing overcharging and deep discharge to protect the battery.
- Battery Stores Energy: The regulated DC electricity is stored in the battery for later use.
- Optional Inverter Converts DC to AC: If needed, an inverter converts DC electricity from the battery into alternating current (AC) for use with standard AC-powered devices and appliances.
- Energy Use: The stored energy can be used directly for DC devices or converted to AC power for household and commercial use.
Types of Solar Battery Chargers
Various solar battery chargers are available on the market, but choosing the right one is key to achieving maximum efficiency.
Portable vs. Stationary
Portable Solar Battery Chargers are compact, lightweight units designed for charging batteries on the go or in remote locations without access to grid power. Portable chargers are ideal for camping, hiking, emergency preparedness kits, and charging electronics during outages. They consist of small solar panels (5-30W) and a built-in charge controller.
Stationary battery chargers are larger systems designed for permanent installation. They are often used in off-grid homes, cabins, RVs, or boats. They feature more powerful solar panel arrays (100W+) connected to charge controllers and a battery bank.
Integrated vs. Modular systems
Integrated systems are all-in-one units that combine solar panels, charge controllers, and batteries into a single enclosure or product. On the other hand, modular systems allow the mixing and matching of separate solar panels, charge controllers, and battery banks based on specific power needs.
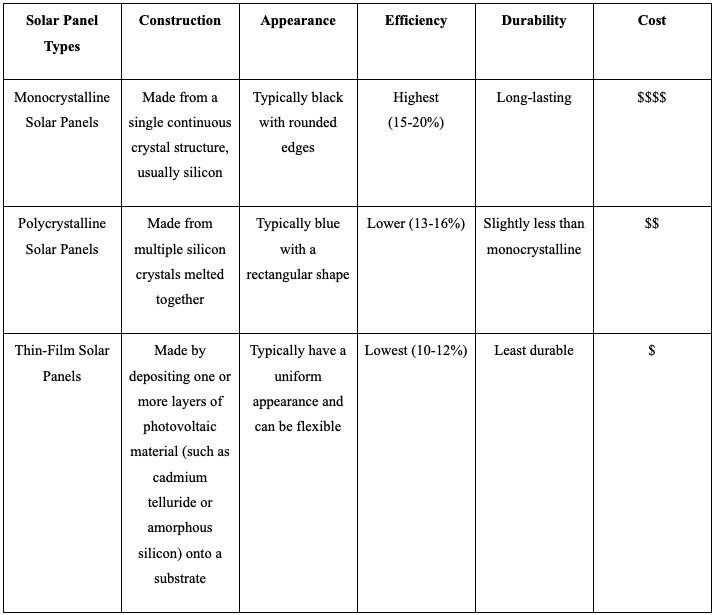
2. Battery Types
There are two main battery types for solar battery chargers: lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. Here is a comparison of their key characteristics.
Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Older technology
- Lower upfront cost
- Two common types: flooded and sealed (AGM or gel)
- Lower energy density
- Shorter lifespan of 3-7 years
- Require more maintenance
- It is not as efficient at charging/discharging as lithium-ion
Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Advanced technology
- Higher upfront cost but a longer lifespan
- Main type: Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP/LiFePO4) due to safety
- Much higher energy density
- Longer lifespan of 5-10 years
- Virtually maintenance-free
- Higher charge/discharge efficiency of around 95%+
3. Charge Control Technologies
The choice between PWM and MPPT charge controllers depends on the specific needs of the solar charging system, including budget, system size, and efficiency requirements. Let’s compare the two charge controllers to better understand the options.
PWM controller
- Efficiency: 70-80%
- Cost: Lower
- Voltage Matching: Matches battery voltage
- Best Use Case: Small systems, close voltage match
- Installation: Simpler
- Performance in Varying Conditions: Lower
MPPT controller
- Efficiency: 95-99%
- Cost: Higher
- Voltage Matching: Matches battery voltage
- Best Use Case: For larger systems, a significant voltage difference
- Installation: More complex
- Performance in Varying Conditions: Higher
A solar charge controller is vital for protecting batteries. It helps prevent overcharging or discharging, optimizes energy use, and protects system components.
What Factors to Consider When Choosing a Solar Battery Charger?
When selecting a solar battery charger, several critical factors must be considered to ensure the system meets your energy needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
1. Energy Needs Assessment
It is important to have a clear idea of the household’s energy consumption to determine the total energy consumption of the devices or appliances that need to be powered with the solar battery charger. This includes reviewing the power draw that each device requires and estimating its typical usage duration.
To simplify things, here is a formula usually used to estimate daily energy consumption.
Daily Energy Consumption (Wh) = Power Rating (W) × Usage Time (hours)
This sums up the energy consumption of all appliances to get the total daily energy consumption.
It is crucial to identify the maximum power demand expected from the system. We must consider whether multiple devices will be running simultaneously on the solar battery, as this peak power demand will influence the sizing of the solar panels and batteries.
2. System Size and Scalability
System size refers to the capacity of the solar battery charger system, including the number of solar panels and the storage capacity of the batteries. Scalability is about how well the system can accommodate increasing energy needs by expanding its capacity with additional panels or batteries.
It’s crucial to choose the right system size so it can meet current energy needs and have the potential to grow as future needs increase. A system that is too small may not provide sufficient power, leading to energy shortages. If it’s too large, it may result in unnecessary expenses. Scalability ensures that the system can be expanded without significant modifications, making it easier to manage increasing energy demands efficiently.
3. Budget and Cost Efficiency
Several cost-efficiency initiatives require an upfront investment. However, the goal remains to consider the long-term savings. The savings generated eventually outweigh these initial costs after the payback period. It is worth noting that the installation cost for solar panels in Canada has gradually decreased over the last five to ten years, making installation costs even lower than upfront payments.
When selecting a solar battery charger system, it is essential to balance the initial investment with long-term savings and consider the return on investment (ROI). While the upfront costs can be significant, the long-term benefits, on factors such as reduced energy bills, maintenance savings, and potential incentives, potentially result in a favorable ROI. Proper assessment of system size, scalability, and careful planning can ensure the investment pays off over time. An easy way to estimate the ROI is to know the total cost and net savings.
4. Installation and Maintenance
Professional installation ensures proper system set-up and integration. However, it increases upfront costs since DIY installation is cheaper but riskier.
Most maintenance costs are minimal for new systems under warranty. However, long-term costs, including bills for cleaning, inspections, repairs, and replacements, should be taken into account over a 25 to 30-year lifespan.

Which Solar Battery Chargers to Consider?
Based on the factors discussed, here are two recommended solar battery chargers that align well with home energy needs, particularly during power outages and emergencies:
1. Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus offers a versatile and expandable capacity ranging from 2 kWh to 24 kWh by adding battery packs and solar panels. This makes it an ideal choice for off-grid living and powering the home during extended blackouts, which are common in Canada due to extreme weather. This generator can be charged with solar energy during power outages, ensuring a reliable power supply. It can power heavy-duty devices up to 6000W, making it suitable for both emergency home use and outdoor activities like camping.
The LiFePO4 Battery, with a 10-year lifespan, offers long-lasting reliability. It provides peace of mind during power outages and enhances the convenience of outdoor adventures. This model ensures that your essential home appliances, like refrigerators, heaters, and communication devices, stay operational during emergencies.
2. Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro
The Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro is a robust power solution with a 3024Wh capacity and 3000W power output, capable of covering almost all household electricity needs. Its ultra-fast charging capabilities and portable design, complete with a pull rod and double wheels, make it ideal for RVs, camping, and home use. The generator’s ability to operate in temperatures as low as -20°C / -4°F makes it particularly suitable for Canadian climates.
Additionally, the Smart App Control feature allows for easy generator management, and its quiet canyon cooling system ensures silent operation. This model is equipped with an upgraded Battery Management System (BMS) for enhanced safety and efficiency. It’s perfect for ensuring continuous power for essential home appliances during blackouts, such as lights, medical devices, and communication equipment, providing a reliable backup power solution.
Conclusion
Solar energy is a clean, renewable, and cost-effective power source. Choosing the right solar battery charger for your home ensures energy independence, reduces utility costs, and provides reliable power during emergencies. You can find the most suitable solution by assessing your energy needs, considering system size, balancing your budget, and planning for proper installation.
Published by: Khy Talara









